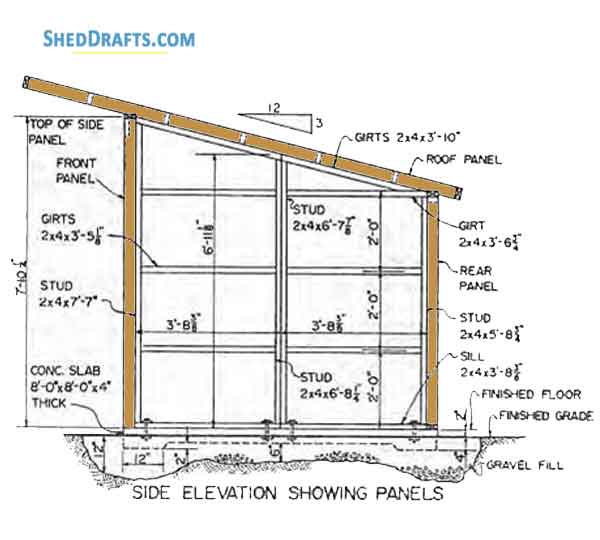
6x8 Lean-To Shed Plans: A Comprehensive Guide to Easy Construction
This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to constructing a 6x8 lean-to shed. Lean-to sheds offer a simple, cost-effective solution for additional storage or workspace, particularly when attached to an existing structure like a house or garage. While seemingly straightforward, proper planning and execution are crucial for a durable and safe structure. This guide emphasizes clarity and practicality, enabling even novice builders to successfully complete this project.
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
Before initiating construction, meticulous planning is paramount. This phase involves several critical steps that will significantly impact the project's success and efficiency.
Site Selection and Assessment
Choosing the appropriate location for your lean-to is the first and arguably most important decision. Consider the following factors:
- Proximity to existing structures: The lean-to needs secure attachment to a sturdy wall. Ensure this wall is capable of supporting the added weight.
- Ground conditions: Level ground is ideal. Uneven terrain necessitates leveling before foundation work commences.
- Access: Ensure easy access for material delivery and construction. Consider potential obstructions.
- Local regulations: Check local building codes and obtain necessary permits before starting construction. This is crucial to avoid legal complications later.
Material Selection and Procurement
Selecting high-quality materials is essential for a durable and long-lasting shed. Consider the following:
- Pressure-treated lumber: Use pressure-treated lumber for the foundation, framing, and any components in direct contact with the ground to resist rot and insect damage.
- Roofing material: Choose a roofing material that suits your budget and aesthetic preferences. Asphalt shingles are a popular and cost-effective option.
- Siding material: Similar to roofing, siding options vary widely. Consider factors like cost, maintenance, and aesthetic appeal when making your choice.
- Fasteners: Use galvanized nails and screws to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Concrete mix: If opting for a concrete foundation, ensure you have enough mix for a solid and level base.
Tool Acquisition and Preparation
Having the right tools is crucial for efficient and safe construction. Ensure you have the following:
- Measuring tape: Accuracy is paramount in construction. A reliable measuring tape is indispensable.
- Level: A level is vital for ensuring the shed's structural integrity. Both a spirit level and a laser level can prove beneficial.
- Shovel: For digging and leveling the ground.
- Hammer: For driving nails.
- Drill/Driver: A drill/driver with various drill bits and screw heads is incredibly helpful.
- Saw (circular or hand saw): For cutting lumber to size.
- Safety glasses and gloves: Always prioritize safety. Wear appropriate safety gear throughout the construction process.
Phase 2: Foundation and Framing
This phase focuses on the structural foundation and framing of your lean-to shed. A robust foundation and correctly framed structure are essential for a stable and long-lasting shed.
Foundation Construction
The foundation provides stability and protects the structure from ground moisture. Several options exist:
- Concrete Slab: This is the most durable option, offering excellent stability. Requires excavation, formwork, and pouring concrete.
- Gravel Base: A simpler and less expensive option. Involves leveling the ground and creating a compacted gravel base.
- Concrete Pier Blocks: A compromise between the two above, offering decent stability at a moderate cost.
Regardless of the chosen foundation, ensure it is level and capable of supporting the shed's weight. Refer to local building codes for specific requirements.
Framing the Walls and Roof
Framing involves constructing the walls and roof structure. Accurate measurements and precise cuts are crucial:
- Wall Framing: Construct the side walls using pressure-treated lumber, ensuring plumbness and squareness at all stages.
- Roof Framing: Construct the roof rafters, ensuring appropriate spacing and proper slope for water runoff. Consider the roof’s load-bearing capacity.
- Attaching to Existing Structure: Securely attach the lean-to to the existing structure using appropriate fasteners and methods. This connection is critical for the shed’s stability.
Phase 3: Exterior Finishing and Roofing
This phase involves completing the exterior of the shed, including the roofing and siding. Careful attention to detail will ensure a weather-resistant and aesthetically pleasing structure.
Roofing Installation
Roofing installation involves laying the chosen roofing material over the framed structure. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure proper installation and prevent leaks.
- Underlayment: Install an underlayment to provide an extra layer of protection against moisture.
- Shingle Installation (or alternative roofing): Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper shingle installation, including proper overlap and nailing techniques.
- Flashing: Install flashing around any penetrations (e.g., vents) to prevent leaks.
Siding Installation
Siding provides protection from the elements and enhances the shed's aesthetic appeal. Choose a siding material that suits your needs and budget, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation.
- Sheathing (if necessary): Install sheathing (e.g., plywood) under the siding for additional structural support and weather protection.
- Siding Application: Attach the siding using appropriate fasteners, ensuring proper alignment and overlap.
Phase 4: Interior Finishing and Details
The final phase involves completing the interior of the shed and adding any necessary details.
Floor Installation
Install a floor using plywood or other suitable material. Ensure the floor is level and securely attached to the framing.
Door and Window Installation (Optional)
If desired, install a door and windows, ensuring proper weather sealing around openings.
Final Touches
Add any final touches such as painting, shelving, or electrical wiring (if permitted and installed by a qualified electrician). Ensure all aspects meet local building codes and regulations.
Constructing a 6x8 lean-to shed requires careful planning and execution. By following these steps and prioritizing safety, even novice builders can successfully complete this rewarding project. Remember to always consult local building codes and regulations before commencing any construction.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.